Q1. What is Design Thinking? Step 3
DESIGN THINKING PROCESS
 A model of the design thinking process is shown as a 5-step process. These steps are not necessarily in the order that people will end up following, sometimes you will need to jump back and forth between steps.
A model of the design thinking process is shown as a 5-step process. These steps are not necessarily in the order that people will end up following, sometimes you will need to jump back and forth between steps.
For example, if someone is not able to complete an accurate test of their solution they may need to jump back to the prototype stage to make a new mock-up to test. We’ll be using this model as our guide to exploring the design thinking process. A design thinking process can help you solve some of the hardest problems or some of the silliest.

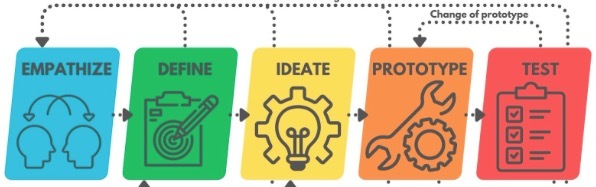
Via canva.com
KEY CONCEPTS
1. Design Thinking is a process for creating solutions for people's needs.
2. There are 5 different stages in the Design Thinking process, but they are not always followed in any order and may need to be repeated multiple times (Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test)
 DESIGN THINKING PROJECT
DESIGN THINKING PROJECT
STEPS
1. Assemble your team.
2. Select the team member that will download or copy the document.
Design Thinking Digital Workbook (slides version) (PDF version)
3. Make sure it is saved and shared with your team and teacher.
4. Complete the Quest 1 What is Design Thinking parts: Assemble Your Team by adding the names of each team member, and saving and sharing it as indicated.
In Quest 2 you will use this Workbook to begin identifying a problem.
 Design Thinking Workbook Image
Design Thinking Workbook Image

Competencies & Standards
MITECS Michigan Integrated Technology Competencies for Students, and
1. Empowered Learner
b. build networks and customize their learning environments
in ways that support the learning process
4. Innovative Designer
a. Know and use a deliberate design process for generating ideas, testing theories, creating innovative artifacts or solving authentic problems
b. Select and use digital tools to plan and manage a design process that considers design constraints and calculated risks
7. Global Collaborator
b. use collaborative technologies to work with others, including peers, experts or community members, to examine issues and problems from multiple viewpoints
c. contribute constructively to project teams, assuming various roles and responsibilities to work effectively toward a common goal
d. explore local and global issues and use collaborative technologies to work with others to investigate solutions
6. Creative Communicator
a. Choose the appropriate platforms and tools for meeting the desired objectives of their creation or communication
Websites and Documents
Websites
- Engineering Design Process
- Fidgits to the Rescue
- Source #1: Teen-Created Software IDs Skin Conditions, Risky Drivers and More
- Source #2: Virginia High School Student Creates Soap to Fight Skin Cancer
- Scientific Method
Videos from Outside Sources
21t4s Videos
21t4s Documents & Quizzes
21t4s Digital Breakout Challenge




